smart card applet java This applet has to be used for uploading and installing new applets. In most cases the used SDK of your JavaCard comes with libraries that encapsulate the necessary steps for .
Mobile access is the use of a mobile device (e.g., smartphone, tablet or wearable) to .
0 · wikipedia java card
1 · what is a java card
2 · microsoft java card
3 · list of javacard apps
4 · java card vm
It does have 2 locations where Card Emulation can happen, the first being in the NFC's Chip Secure Element (an independent CPU) or on the Host CPU (Hence the term Host .
A Java Card PKI Applet aiming to be ISO 7816 compliant. The Applet is capable of saving a PKCS#15 file structure and performing PKI related operations using the private key, such as .Issues 6 - Curated list of JavaCard applications - GitHubPull requests - Curated list of JavaCard applications - GitHubReleases - Curated list of JavaCard applications - GitHub
This is applet for smartcards supporting JavaCard platform. This applet was . This applet has to be used for uploading and installing new applets. In most cases the used SDK of your JavaCard comes with libraries that encapsulate the necessary steps for .
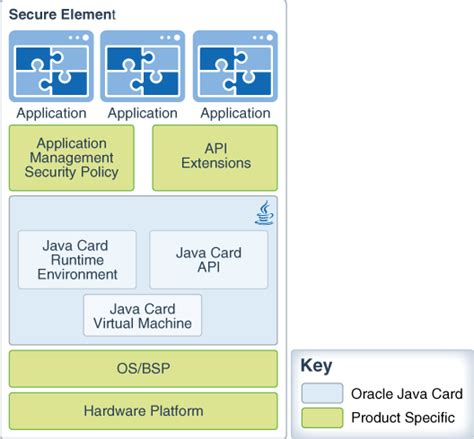
Java Card aims at defining a standard smart card computing environment allowing the same Java Card applet to run on different smart cards, much like a Java applet runs on different computers. As in Java, this is accomplished using the combination of a virtual machine (the Java Card Virtual Machine), and a well-defined runtime library, which largely abstracts the applet from differences between smart cards. Portability remains mitigated by issues of memory size, performance, an.
Learn the programming concepts and major steps of creating Java Card applets. This article walks you through the process of creating a simple electronic wallet applet and .An off-card installer for installing a Java Card applet onto a smart card. Using these classes and tools, you develop a Java Card applet on your workstation or PC. Specifically, you: Compile . The following seven steps comprise the whole applet development phase, including completing your applet project and running your applet on a real smart card. Step 1. Set up . Java Card technology adapts the Java platform for use on smart cards and other devices whose environments are highly specialized, and whose memory and processing .
Since a smart card does not have a user interface, you either need a smart card reader to read and write the data on your cards, or use the emulator included in the Java Card Reference .This is applet for smartcards supporting JavaCard platform. This applet was created as a part of a Bachelor thesis focused on obtaining powertraces of basic cryptografic operations. Each .A Java Card PKI Applet aiming to be ISO 7816 compliant. The Applet is capable of saving a PKCS#15 file structure and performing PKI related operations using the private key, such as signing or decrypting. Private keys can be generated directly on the smartcard or imported from the host computer. This applet has to be used for uploading and installing new applets. In most cases the used SDK of your JavaCard comes with libraries that encapsulate the necessary steps for selecting the CardManager (including necessary authentication), loading and installing an applet.
Java Card aims at defining a standard smart card computing environment allowing the same Java Card applet to run on different smart cards, much like a Java applet runs on different computers. As in Java, this is accomplished using the combination of a virtual machine (the Java Card Virtual Machine), and a well-defined runtime library, which .
This article introduces smart cards, gives a brief overview of Java Card technology, and by stepping you through the code of a sample applet distributed with a Java Card toolkit, shows you how to code a Java Card applet. Learn the programming concepts and major steps of creating Java Card applets. This article walks you through the process of creating a simple electronic wallet applet and provides.An off-card installer for installing a Java Card applet onto a smart card. Using these classes and tools, you develop a Java Card applet on your workstation or PC. Specifically, you: Compile the applet. Optionally, test the applet in the JCWDE, and debug the applet. Convert the applet. The following seven steps comprise the whole applet development phase, including completing your applet project and running your applet on a real smart card. Step 1. Set up java card development environment
Java Card technology adapts the Java platform for use on smart cards and other devices whose environments are highly specialized, and whose memory and processing constraints are typically more severe than those of J2ME devices. Smart cards are very useful in the areas of personal security.Since a smart card does not have a user interface, you either need a smart card reader to read and write the data on your cards, or use the emulator included in the Java Card Reference Implementation (RI). This tutorial will use the emulator.This is applet for smartcards supporting JavaCard platform. This applet was created as a part of a Bachelor thesis focused on obtaining powertraces of basic cryptografic operations. Each cryptographic operation is delimited by operations of random number generation.A Java Card PKI Applet aiming to be ISO 7816 compliant. The Applet is capable of saving a PKCS#15 file structure and performing PKI related operations using the private key, such as signing or decrypting. Private keys can be generated directly on the smartcard or imported from the host computer.
This applet has to be used for uploading and installing new applets. In most cases the used SDK of your JavaCard comes with libraries that encapsulate the necessary steps for selecting the CardManager (including necessary authentication), loading and installing an applet.Java Card aims at defining a standard smart card computing environment allowing the same Java Card applet to run on different smart cards, much like a Java applet runs on different computers. As in Java, this is accomplished using the combination of a virtual machine (the Java Card Virtual Machine), and a well-defined runtime library, which .
This article introduces smart cards, gives a brief overview of Java Card technology, and by stepping you through the code of a sample applet distributed with a Java Card toolkit, shows you how to code a Java Card applet.
Learn the programming concepts and major steps of creating Java Card applets. This article walks you through the process of creating a simple electronic wallet applet and provides.
An off-card installer for installing a Java Card applet onto a smart card. Using these classes and tools, you develop a Java Card applet on your workstation or PC. Specifically, you: Compile the applet. Optionally, test the applet in the JCWDE, and debug the applet. Convert the applet.
The following seven steps comprise the whole applet development phase, including completing your applet project and running your applet on a real smart card. Step 1. Set up java card development environment Java Card technology adapts the Java platform for use on smart cards and other devices whose environments are highly specialized, and whose memory and processing constraints are typically more severe than those of J2ME devices. Smart cards are very useful in the areas of personal security.
Since a smart card does not have a user interface, you either need a smart card reader to read and write the data on your cards, or use the emulator included in the Java Card Reference Implementation (RI). This tutorial will use the emulator.
scanning fendi rfid tag

wikipedia java card
what is a java card
Clipper is the all-in-one transit card used for contactless fare payments throughout .
smart card applet java|java card vm