what are some radio frequency identification chip advances A passive harmonic RFID exploits the frequency orthogonality of the transmitted (fundamental tone) and received (harmonics) radio-frequency (RF) signals to enable robust interrogation in noisy and cluttered environments, not possible with traditional passive linear RFIDs. $29.99
0 · where are rfid chips used
1 · what is meant by rfid
2 · radio frequency tracking
3 · radio frequency identification tags are
4 · radio frequency identification readers
5 · radio frequency identification examples
6 · how do rfid chips work
7 · define radio frequency identification tag
The place to discuss all stuff related to the Nintendo 3DS™ family! . Of course, it was made .
A passive harmonic RFID exploits the frequency orthogonality of the transmitted (fundamental tone) and received (harmonics) radio-frequency (RF) signals to enable robust interrogation in noisy and cluttered environments, not possible with traditional passive linear RFIDs.
Clutter and localization issues can be substantially mitigated by employing a harmonic RFID solution. The harmonic RFID tag and reader operates at two different .
RFID (radio frequency identification) technology appeared nearly 70 years ago. Deployed more widely only from the early 2000s, it is now booming and its development is still .
A passive harmonic RFID exploits the frequency orthogonality of the transmitted (fundamental tone) and received (harmonics) radio-frequency (RF) signals to enable robust interrogation in noisy and cluttered environments, not possible with traditional passive linear RFIDs. Clutter and localization issues can be substantially mitigated by employing a harmonic RFID solution. The harmonic RFID tag and reader operates at two different frequencies: (a) reader to tag downlink at the fundamental frequency, and (b) tag to reader uplink at the harmonic frequency. Radio-frequency identification (RFID) has come a long way in the past few years, but this exciting tech revolution is only just beginning. Already, RFID is crucial in manufacturing , retail, and even healthcare. RFID (radio frequency identification) technology appeared nearly 70 years ago. Deployed more widely only from the early 2000s, it is now booming and its development is still accelerating.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is considered as a new sensing paradigm due to its low-cost, passive wireless power transfer capability, flexibility, and non-line-of-sight communication. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) sensors, integrating the features of Wireless Information and Power Transfer (WIPT), object identification and energy efficient sensing capabilities, have been considered a new paradigm of sensing and communication for the futuristic information systems.
The RFID (Radio Frequency IDentification) technology is a well-known wireless application for traceability, logistics, and access control. It became ubiquitous in industry and our daily life (ticketing, payment, passports, car keys, etc.).Radio frequency identification (RFID) is a means of identifying objects by interrogating a unique characteristic of the object (such as a unique identifying number stored on a silicon chip attached to the object) using radio waves. 1 This technology promises orders-of-magnitude greater efficiency and accuracy than were possible previous . Research into eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient operations can contribute to more sustainable RFID solutions. Application-Specific Innovations: Tailoring RFID solutions to specific industry needs, such as healthcare, retail, and .
Application software, including a server, antenna, transponders, and readers, are the essential components of radio frequency identification technology. The technology for identification of radio frequency signals is a small antenna-based microchip.A passive harmonic RFID exploits the frequency orthogonality of the transmitted (fundamental tone) and received (harmonics) radio-frequency (RF) signals to enable robust interrogation in noisy and cluttered environments, not possible with traditional passive linear RFIDs. Clutter and localization issues can be substantially mitigated by employing a harmonic RFID solution. The harmonic RFID tag and reader operates at two different frequencies: (a) reader to tag downlink at the fundamental frequency, and (b) tag to reader uplink at the harmonic frequency. Radio-frequency identification (RFID) has come a long way in the past few years, but this exciting tech revolution is only just beginning. Already, RFID is crucial in manufacturing , retail, and even healthcare.
fitbit 6 nfc reader
RFID (radio frequency identification) technology appeared nearly 70 years ago. Deployed more widely only from the early 2000s, it is now booming and its development is still accelerating. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is considered as a new sensing paradigm due to its low-cost, passive wireless power transfer capability, flexibility, and non-line-of-sight communication.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) sensors, integrating the features of Wireless Information and Power Transfer (WIPT), object identification and energy efficient sensing capabilities, have been considered a new paradigm of sensing and communication for the futuristic information systems.
The RFID (Radio Frequency IDentification) technology is a well-known wireless application for traceability, logistics, and access control. It became ubiquitous in industry and our daily life (ticketing, payment, passports, car keys, etc.).
developed an nfc label
Radio frequency identification (RFID) is a means of identifying objects by interrogating a unique characteristic of the object (such as a unique identifying number stored on a silicon chip attached to the object) using radio waves. 1 This technology promises orders-of-magnitude greater efficiency and accuracy than were possible previous . Research into eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient operations can contribute to more sustainable RFID solutions. Application-Specific Innovations: Tailoring RFID solutions to specific industry needs, such as healthcare, retail, and .
where are rfid chips used
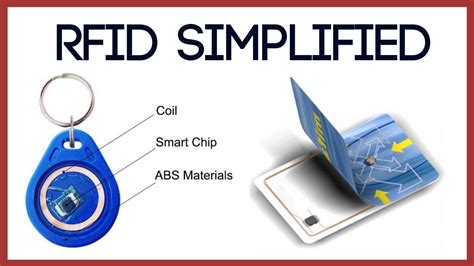
what is meant by rfid
nfc reader and writer
$25.79
what are some radio frequency identification chip advances|define radio frequency identification tag