how is a rfid chip powered RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person. NFC technology that uses radio waves to transmit data from the consumer’s card to the merchant’s terminal. NFC is a subset of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID). But, unlike other RFID-enabled technologies, which can .
0 · what is meant by rfid
1 · rfid is involved when using
2 · rfid definition computer
3 · radio frequency identification rfid tag
4 · radio frequency identification examples
5 · radio frequency identification chips
6 · how does rfid scanning work
7 · how do rfid cards work
To use their smartphones to pay for public transport fares, commuters holding the selected NFC-enabled devices need to first get a new SIM card, priced at S$37.45 by all three telcos. M1 started .
RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.Data stored within an RFID tag's microchip waits to be read. The tag's antenna receives electromagnetic energy from an RFID reader's antenna. Using power from its internal battery or power harvested from the reader's electromagnetic field, the tag sends radio waves back to . A small chip -- known as an RFID tag -- is attached to or implanted in an object. The tags contain information that can be read at short range via radio waves. The chip and reader don't have to touch. Some RFID tags can be powered by a .
Radio and television involve sending radio waves in one direction only: from the transmitter at the radio or TV station to the receiver (the radio or TV set) in your home. Wireless Internet and cellphones are more sophisticated because they involve two-way communication. RFID chips operate based on the principle of radio waves. When an RFID reader emits radio waves, the antenna on the chip captures the waves, converting them into electrical energy. This energy powers the microchip, allowing it to perform various functions, including storing and transmitting data.
An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter. When triggered by an electromagnetic interrogation pulse from a nearby RFID reader device, the tag transmits digital data, usually an identifying inventory number, back to the reader. RFID enables seamless and automated tracking of assets, products, and personnel, enhancing security and supply chain visibility. It also enhances customer experiences by enabling personalized interactions and streamlined checkout processes. RFID technology uses small chips to store and transmit information wirelessly for tracking and identification purposes. Learn all about RFID.When a passive RFID chip enters the electromagnetic field of an RFID reader, it absorbs energy from the reader’s signal. This energy is used to power the chip’s circuitry, allowing it to transmit its unique identifier or other stored data back to the reader.
RFID is an acronym for “radio-frequency identification” and refers to a technology whereby digital data encoded in RFID tags or smart labels (defined below) are captured by a reader via radio waves. RFID is similar to barcoding in that data from a tag or label are captured by a device that stores the data in a database.RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.Data stored within an RFID tag's microchip waits to be read. The tag's antenna receives electromagnetic energy from an RFID reader's antenna. Using power from its internal battery or power harvested from the reader's electromagnetic field, the tag sends radio waves back to . A small chip -- known as an RFID tag -- is attached to or implanted in an object. The tags contain information that can be read at short range via radio waves. The chip and reader don't have to touch. Some RFID tags can be powered by a .
Radio and television involve sending radio waves in one direction only: from the transmitter at the radio or TV station to the receiver (the radio or TV set) in your home. Wireless Internet and cellphones are more sophisticated because they involve two-way communication.
what is meant by rfid
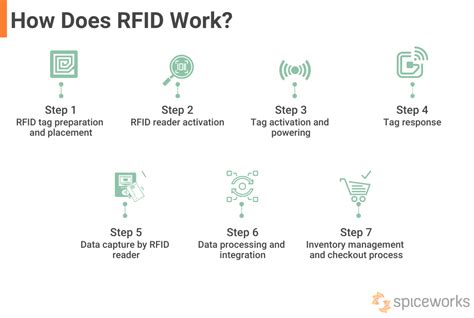
rfid is involved when using
RFID chips operate based on the principle of radio waves. When an RFID reader emits radio waves, the antenna on the chip captures the waves, converting them into electrical energy. This energy powers the microchip, allowing it to perform various functions, including storing and transmitting data.An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter. When triggered by an electromagnetic interrogation pulse from a nearby RFID reader device, the tag transmits digital data, usually an identifying inventory number, back to the reader.

RFID enables seamless and automated tracking of assets, products, and personnel, enhancing security and supply chain visibility. It also enhances customer experiences by enabling personalized interactions and streamlined checkout processes.
RFID technology uses small chips to store and transmit information wirelessly for tracking and identification purposes. Learn all about RFID.When a passive RFID chip enters the electromagnetic field of an RFID reader, it absorbs energy from the reader’s signal. This energy is used to power the chip’s circuitry, allowing it to transmit its unique identifier or other stored data back to the reader.

rfid definition computer

fitness band nfc google pay
Luna Marked Flash Poker Cards Introducing our premium quality paper Luna Cards. We are .
how is a rfid chip powered|radio frequency identification examples