components of rfid system pdf [RFID Handbuch. English] Fundamentals and Applications in Contactless Smart Cards, Radio Frequency Identification and Near-Field Communication, Third Edition / Klaus Finkenzeller ; translated by Dorte M¨ ¨uller. – 3rd ed. p. cm. Includes index. ISBN 978-0-470-69506-7 (cloth) 1. Inventory control–Automation. 2. Radio frequency . The latest update is all about RFID and NFC, and how the Flipper Zero can interact with a variety of contactless protocols. Contactless tags are broadly separated into low-frequency (125 kHz) and .
0 · types of rfid systems
1 · types of rfid readers
2 · select three rfid system parts
3 · rfid systems for small business
4 · rfid radio frequency identification
5 · rfid principles and components
6 · rfid in embedded system
7 · rfid full form in computer
OptiPlex 3060 Tower, OptiPlex 3060 Micro, OptiPlex 3060 Small Form Factor, OptiPlex 5070 Tower, OptiPlex 5070 Micro, OptiPlex 5070 Small Form Factor, OptiPlex 7060 .Method 2: Looking for signs on the card: Some cards may have visible indications indicating the presence of RFID or NFC technology. Look for any logos or symbols on the card that suggest contactless communication. .
types of rfid systems
An RFID system consists of an RFID reader, RFID tag, and information man- aging host computer. The reader contains an RF transceiver module (transmit- ter and receiver), a signal .RFID component parts are: Tag or transponder: a RFID tag is a tiny radio device that is also referred to as a transponder, smart tag, smart label or radio bar code. The tag comprises a .
types of rfid readers
We present a brief history of RFID technology and automatic identification systems. We summarize major RFID applications, and present a primer on RFID fundamental .
[RFID Handbuch. English] Fundamentals and Applications in Contactless Smart Cards, Radio Frequency Identification and Near-Field Communication, Third Edition / Klaus Finkenzeller ; translated by Dorte M¨ ¨uller. – 3rd ed. p. cm. Includes index. ISBN 978-0-470-69506-7 (cloth) 1. Inventory control–Automation. 2. Radio frequency .
An RFID system consists of an RFID reader, RFID tag, and information man- aging host computer. The reader contains an RF transceiver module (transmit- ter and receiver), a signal processor and controller unit, a coupling element (antenna), and a serial data interface (RS232, RS485) to a host system.
RFID component parts are: Tag or transponder: a RFID tag is a tiny radio device that is also referred to as a transponder, smart tag, smart label or radio bar code. The tag comprises a simple silicon microchip (typically less than half a millimetre in size) attached to a small flat aerial and mounted on a substrate.
We present a brief history of RFID technology and automatic identification systems. We summarize major RFID applications, and present a primer on RFID fundamental principles. Finally, we discuss several challenges and obstacles to RFID adoption, as well as emerging technologies relevant to RFID.typical RFID system is comprised of the following components: One or more tags or transponders with unique identification codes and a small antenna embedded within each tag.
The basic RFID system consists of a Reader and a Transponder. The Reader or Transceiver is the unit acting as the master and supplies the RFID transponder with energy and triggers the communication signals to force the transponder to execute the requested action.
select three rfid system parts
This white paper describes the basic components of a Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) system and explores the technology, applications, and competitive advantages of RFID technology and its uses for Automatic Identification Data Collection (AIDC). 1.A basic RFID system consists of three components: • An antenna or coil • A transceiver (with decoder) • A transponder (RF tag) electronically programmed with unique information There are two types of transponders, which correlate to the two major types of RFID tags. • Passive transponders and RFID tags have no energyKey topics such as performance optimization and evaluation, sensors, network simulation, RFID in the retail supply chain, and testing are covered, as are applications in product lifecycle management in the automotive and aerospace sectors, in anti-counterfeiting, and in health care.Using an RFID system allows consolidated management of objects and information. Purposes of using RFID in a production site mainly comprises the following applications. Work instruction (destination instruction) History management (production history, work .
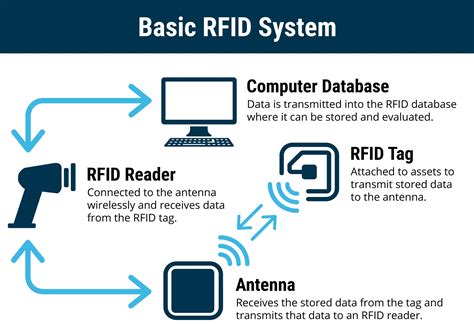
[RFID Handbuch. English] Fundamentals and Applications in Contactless Smart Cards, Radio Frequency Identification and Near-Field Communication, Third Edition / Klaus Finkenzeller ; translated by Dorte M¨ ¨uller. – 3rd ed. p. cm. Includes index. ISBN 978-0-470-69506-7 (cloth) 1. Inventory control–Automation. 2. Radio frequency .An RFID system consists of an RFID reader, RFID tag, and information man- aging host computer. The reader contains an RF transceiver module (transmit- ter and receiver), a signal processor and controller unit, a coupling element (antenna), and a serial data interface (RS232, RS485) to a host system.RFID component parts are: Tag or transponder: a RFID tag is a tiny radio device that is also referred to as a transponder, smart tag, smart label or radio bar code. The tag comprises a simple silicon microchip (typically less than half a millimetre in size) attached to a small flat aerial and mounted on a substrate.
We present a brief history of RFID technology and automatic identification systems. We summarize major RFID applications, and present a primer on RFID fundamental principles. Finally, we discuss several challenges and obstacles to RFID adoption, as well as emerging technologies relevant to RFID.
typical RFID system is comprised of the following components: One or more tags or transponders with unique identification codes and a small antenna embedded within each tag.
The basic RFID system consists of a Reader and a Transponder. The Reader or Transceiver is the unit acting as the master and supplies the RFID transponder with energy and triggers the communication signals to force the transponder to execute the requested action.This white paper describes the basic components of a Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) system and explores the technology, applications, and competitive advantages of RFID technology and its uses for Automatic Identification Data Collection (AIDC). 1.A basic RFID system consists of three components: • An antenna or coil • A transceiver (with decoder) • A transponder (RF tag) electronically programmed with unique information There are two types of transponders, which correlate to the two major types of RFID tags. • Passive transponders and RFID tags have no energyKey topics such as performance optimization and evaluation, sensors, network simulation, RFID in the retail supply chain, and testing are covered, as are applications in product lifecycle management in the automotive and aerospace sectors, in anti-counterfeiting, and in health care.
what is meant by smart card system

rfid systems for small business
rfid radio frequency identification
rfid principles and components
Moneto is an NFC-based mobile payment system developed by DeviceFidelity .
components of rfid system pdf|select three rfid system parts