how to read an rf factor in chromatography It is possible to determine the characteristic rate of movement of each substance on the chromatography paper as the moving phase moves at a certain temperature and for a specific solvent. This is represented by the R f value, which stands for relative front or retardation factor. For restaurants, scanning the NFC tag will open up their full menu. Moreover, some individuals use NFC tags as their virtual business cards. So just look for NFC tags. Then try to scan them. It’s a fast and easy way to test if .
0 · why rf value not good
1 · why is rf importnat chemistry
2 · why are rf values useful
3 · what is rf value chromatography
4 · what does rf value mean
5 · rf value in paper chromatography
6 · how to measure rf values
7 · how to calculate rf values
For the NFL’s 2024/2025 season, 14 teams will make the Playoffs: Seven teams from the NFC, and seven teams from the AFC, which breaks down to four division winners and three wild .
It is possible to determine the characteristic rate of movement of each substance on the chromatography paper as the moving phase moves at a certain temperature and for a specific solvent. This is represented by the R f value, which stands for relative front or retardation factor.A convenient way for chemists to report the results of a TLC plate in lab notebooks is through a "retention factor",\(^2\) or \(R_f\) value, which quantitates a compound's movement (Equation \ref{2}). In this article we will learn about Rf value also known as Retention Factor. Here we will discuss calculation of Rf values and its importance in thin layer chromatography. Key .Learn about the Rf value, a key parameter in chromatography that allows for the identification and analysis of individual components in a mixture. Discover why the Rf value is important, how it's .
In thin-layer chromatography, the retention factor (Rf) is used to compare and help identify compounds. The Rf value of a compound is equal to the distance traveled by the compound . Retention Factor. After a separation is complete, individual compounds appear as spots separated vertically. Each spot has a retention factor (Rf) which is equal to the distance migrated over the total distance covered by .In planar chromatography in particular, the retardation factor R F is defined as the ratio of the distance traveled by the center of a spot to the distance traveled by the solvent front. [2] .It is possible to determine the characteristic rate of movement of each substance on the chromatography paper as the moving phase moves at a certain temperature and for a specific solvent. This is represented by the R f value, which stands for relative front or retardation factor.
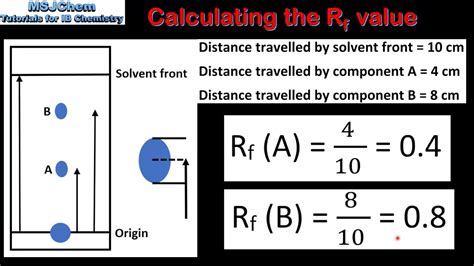
A convenient way for chemists to report the results of a TLC plate in lab notebooks is through a "retention factor",\(^2\) or \(R_f\) value, which quantitates a compound's movement (Equation \ref{2}). In this article we will learn about Rf value also known as Retention Factor. Here we will discuss calculation of Rf values and its importance in thin layer chromatography. Key words: Rf value or Retention factor, Thin layer chromatography (TLC), . In thin layer chromatography, retention factor (Rf) is the distance that a compound travels through the stationary phase (TLC plate) between the origin spot and the distance the solvent front moved above the origin.Learn about the Rf value, a key parameter in chromatography that allows for the identification and analysis of individual components in a mixture. Discover why the Rf value is important, how it's calculated, and the factors that influence it.
In thin-layer chromatography, the retention factor (Rf) is used to compare and help identify compounds. The Rf value of a compound is equal to the distance traveled by the compound divided by the distance traveled by the solvent front (both measured from the origin). Retention Factor. After a separation is complete, individual compounds appear as spots separated vertically. Each spot has a retention factor (Rf) which is equal to the distance migrated over the total distance covered by the solvent. The \( R_f\) formula is \[ R_f= \dfrac{\text{distance traveled by sample}}{\text{distance traveled by solvent}} \]
In planar chromatography in particular, the retardation factor R F is defined as the ratio of the distance traveled by the center of a spot to the distance traveled by the solvent front. [2] Ideally, the values for R F are equivalent to the R values used in column chromatography. [2]Rf values, or the Retention Factor, is a ratio used to describe the relationship between the distance moved by components in a mixture relative to the distance moved by the solvent. It is calculated by dividing the distance moved by the component . Learn how to calculate and interpret RF values in chromatography with our comprehensive educational guide. Master the principles of RF values and their significance in analytical chemistry.It is possible to determine the characteristic rate of movement of each substance on the chromatography paper as the moving phase moves at a certain temperature and for a specific solvent. This is represented by the R f value, which stands for relative front or retardation factor.
A convenient way for chemists to report the results of a TLC plate in lab notebooks is through a "retention factor",\(^2\) or \(R_f\) value, which quantitates a compound's movement (Equation \ref{2}). In this article we will learn about Rf value also known as Retention Factor. Here we will discuss calculation of Rf values and its importance in thin layer chromatography. Key words: Rf value or Retention factor, Thin layer chromatography (TLC), . In thin layer chromatography, retention factor (Rf) is the distance that a compound travels through the stationary phase (TLC plate) between the origin spot and the distance the solvent front moved above the origin.
Learn about the Rf value, a key parameter in chromatography that allows for the identification and analysis of individual components in a mixture. Discover why the Rf value is important, how it's calculated, and the factors that influence it.In thin-layer chromatography, the retention factor (Rf) is used to compare and help identify compounds. The Rf value of a compound is equal to the distance traveled by the compound divided by the distance traveled by the solvent front (both measured from the origin). Retention Factor. After a separation is complete, individual compounds appear as spots separated vertically. Each spot has a retention factor (Rf) which is equal to the distance migrated over the total distance covered by the solvent. The \( R_f\) formula is \[ R_f= \dfrac{\text{distance traveled by sample}}{\text{distance traveled by solvent}} \]
In planar chromatography in particular, the retardation factor R F is defined as the ratio of the distance traveled by the center of a spot to the distance traveled by the solvent front. [2] Ideally, the values for R F are equivalent to the R values used in column chromatography. [2]Rf values, or the Retention Factor, is a ratio used to describe the relationship between the distance moved by components in a mixture relative to the distance moved by the solvent. It is calculated by dividing the distance moved by the component .
open cash app nfc tag
why rf value not good
why is rf importnat chemistry
why are rf values useful

Open Apple Wallet. Select your employee badge. Tap the employee badge on the reader. For an Apple Watch, double-click the side button and scroll down to your badge. Select and scan on the reader. Alternatively, .
how to read an rf factor in chromatography|why is rf importnat chemistry