how do rfid tags modulate Modern diodes can operate up to over 1 GHz, allowing passive RFID tags to demodulate a reader signal using only a diode and capacitor. Unmodified OOK is admirably simple and seems promising as a method of modulating a reader signal.
NFC Key fobs NFC Gadgets. . The most resistant NFC Tag, for industrial use. .
0 · rfid modulation techniques
1 · rfid modulation examples
2 · rfid modulation and multiplexing
3 · rfid encoding
4 · rfid coding methods
5 · ee times rfid modules
The Cash app NFC tag notification signifies that the app has detected a nearby NFC tag. NFC, or Near Field Communication, is a short-range wireless technology that allows electronic devices to communicate with each .
Using a single medium for many signals is known as multiplexing. The most common form of multiplexing in radio, in use for almost a century, is frequency-division multiple access (FDMA): different users transmit using different carrier frequencies, and receivers are adapted to capture only the . See moreThis scheme would seem to allow an unlimited number of users to share the electromagnetic spectrum. However, recall that a signal must be modulated in order to convey information. When we modulate the signal, we increase the signal bandwidth. We saw . See more
Finally, the way we code the signal also matters. By examination of Figure 3.6 and Figure 3.8, we can see that pulse interval encoding will result in shorter pulses than OOK for the same . See moreTo clarify why this sort of thing matters in real applications, let’s look at a practical example. In the United States, unlicensed readers randomly . See more The microchip in a passive RFID tag consists of memory and a modulation circuit. The memory holds the information that is programmed onto the tag, such as a unique identifier or product details. The modulation circuit . Modern diodes can operate up to over 1 GHz, allowing passive RFID tags to demodulate a reader signal using only a diode and capacitor. Unmodified OOK is admirably simple and seems promising as a method of modulating a reader signal.
The microchip in a passive RFID tag consists of memory and a modulation circuit. The memory holds the information that is programmed onto the tag, such as a unique identifier or product details. The modulation circuit modifies the RF signal received by the antenna and encodes the data stored in the memory onto it.
Backscatter is a method of communication in which an RFID tag without a battery (or any internal power source) receives energy from an RFID reader’s transmission and uses that same energy to send back a reply. The tag receives the energy via electromagnetic waves propagated from the reader/antenna. RFID tags (passive tags) do get power from the reader, but they do not transmit a radio signal. Instead what they do is modulate the energy coming from the reader and that changes the load on the reader.
An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter. When triggered by an electromagnetic interrogation pulse from a nearby RFID reader device, the tag transmits digital data, usually an identifying inventory number, back to the reader.
The tag is composed of an antenna coil and a silicon chip that includes basic modulation circuitry and non-volatile memory. The tag is energized by a time-varying electromagnetic radio frequency (RF) wave that is transmitted by the reader. This RF signal is called a carrier signal.
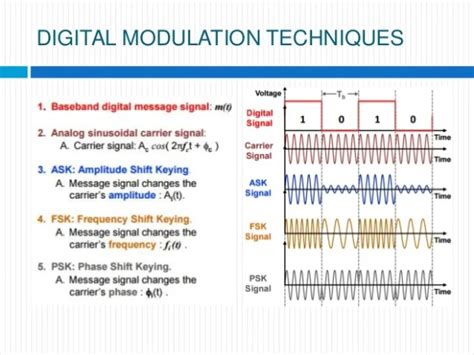
The procedures used in RFID systems are the digital modulation procedures amplitude shift keying (ASK), 2 frequency shift keying (2 FSK) and 2 phase shift keying (2 PSK). The use of a modulated subcarrier is widespread in radio technology. 1. Modulation. RFID tags and readers communicate through the modulation of radio waves. This communication occurs by changing the amplitude of radio waves through Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK). 2. Coding. Through coding, The 1’s and 0’s (bits) of binary code translate into radio transmissions through Amplitude Shift Keying.
Modern diodes can operate up to over 1 GHz, allowing passive RFID tags to demodulate a reader signal using only a diode and capacitor. Unmodified OOK is admirably simple and seems promising as a method of modulating areader signal.How Does RF Field Power Impact Passive RFID? Passive RFID tags derive all of their operating power from the energy of the RF field as absorbed by their antennae.
Modern diodes can operate up to over 1 GHz, allowing passive RFID tags to demodulate a reader signal using only a diode and capacitor. Unmodified OOK is admirably simple and seems promising as a method of modulating a reader signal. The microchip in a passive RFID tag consists of memory and a modulation circuit. The memory holds the information that is programmed onto the tag, such as a unique identifier or product details. The modulation circuit modifies the RF signal received by the antenna and encodes the data stored in the memory onto it.
Backscatter is a method of communication in which an RFID tag without a battery (or any internal power source) receives energy from an RFID reader’s transmission and uses that same energy to send back a reply. The tag receives the energy via electromagnetic waves propagated from the reader/antenna. RFID tags (passive tags) do get power from the reader, but they do not transmit a radio signal. Instead what they do is modulate the energy coming from the reader and that changes the load on the reader.An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter. When triggered by an electromagnetic interrogation pulse from a nearby RFID reader device, the tag transmits digital data, usually an identifying inventory number, back to the reader.
The tag is composed of an antenna coil and a silicon chip that includes basic modulation circuitry and non-volatile memory. The tag is energized by a time-varying electromagnetic radio frequency (RF) wave that is transmitted by the reader. This RF signal is called a carrier signal.
The procedures used in RFID systems are the digital modulation procedures amplitude shift keying (ASK), 2 frequency shift keying (2 FSK) and 2 phase shift keying (2 PSK). The use of a modulated subcarrier is widespread in radio technology. 1. Modulation. RFID tags and readers communicate through the modulation of radio waves. This communication occurs by changing the amplitude of radio waves through Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK). 2. Coding. Through coding, The 1’s and 0’s (bits) of binary code translate into radio transmissions through Amplitude Shift Keying.
Modern diodes can operate up to over 1 GHz, allowing passive RFID tags to demodulate a reader signal using only a diode and capacitor. Unmodified OOK is admirably simple and seems promising as a method of modulating areader signal.
rfid modulation techniques
rfid modulation examples
Opening the NFC tag reader tells your phone to actively search for the NFC tag as it cannot search for it in the background. NFC tag readers allow you to unlock the potential of App Clips on your iPhone.
how do rfid tags modulate|rfid modulation examples