passive rfid tag backscatter When diving deeper into backscatter, it is impossible to leave out the presence and use of an electric field versus exclusively using a magnetic field. The three most used frequencies for RFIDare Low-Frequency (LF), High-Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High . See more Here’s how you can access the NFC Tag Reader on your iPhone and use it not just for the payments but also for so may other things and automate a lot of tasks.
0 · what is backscatter
1 · rfid backscatter equation
2 · backscattering rfid tags
3 · backscatter vs magnetic
4 · backscatter reverse link
5 · backscatter frequency
Discover all radio stations from Alabama and listen to them online. Live internet radio - easy and for free on radio.net. . Montgomery AL, Hip Hop, Rap, R'n'B, Soul. AllWorship. Birmingham, .
what is backscatter
This article walks through the basics and advanced principles related to how UHF RFID Passive tags communicate via backscatter. Before reading, it is important to know about the types of coupling and when each one is used. If you do not know what coupling is and how it works, please refer to " Principles of . See moreBackscatter is a method of communication in which an RFID tagwithout a battery (or any internal power source) receives energy from an RFID . See more
For more information on RFID, comment below or contact us! If you would like to learn more about all things RFID, check out our website or our YouTube channel. To read more about . See more
lost my smart shopper card
When diving deeper into backscatter, it is impossible to leave out the presence and use of an electric field versus exclusively using a magnetic field. The three most used frequencies for RFIDare Low-Frequency (LF), High-Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High . See moreIn order to read multiple tags simultaneously, the tag and reader must be designed to detect . This article walks through the basics and advanced principles related to how UHF RFID Passive tags communicate via backscatter. Before reading, it is important to know about the types of coupling and when each one is used.In order to read multiple tags simultaneously, the tag and reader must be designed to detect the condition that more than one tag is active. Otherwise, the tags will all backscatter the carrier at the same time, and the amplitude-modulated waveforms shown in Figures 3 and 4 would be garbled. This is referred to as a collision.
We derive a theoretical formula for RCS of an RFID tag with a minimum scattering antenna and describe an experimental measurement technique which involves using a network analyzer connected to an anechoic chamber with and without the tag.Since there is not enough field power to operate a traditional RF transmission, passive RFID tags communicate back to the reader with a technique called ‘backscatter’. In effect, what the tag does is alter the impedance of the antenna match so that more or less energy is reflected.
This paper proposed a novel tag circuit design for amplitude-shift keying (ASK) modulation. Instead of using the conventional resistive modulator, we proposed a reactive modulator for impedance matching and backscattered signal modulation. In the past two decades, point-to-point BackCom has been widely deployed in the application of radio-frequency identification (RFID) for a passive RFID tag to report an ID to an enquiring Reader over the near field (typically several centimeters).
Traditional passive UHF RFID tags employ either ASK or PSK backscatter modulation to communicate data from memory or sensors on the tag to a remotely-located reader.RCID: Fingerprinting Passive RFID Tags via Wideband Backscatter Abstract: Tag cloning and spoofing pose great challenges to RFID applications. This paper presents the design and evaluation of RCID, a novel system to fingerprint RFID tags based on the unique reflection coefficient of each tag circuit. To validate this model, we propose a backscatter calibration device to enable measurements with estimated 0.5 dB uncertainty. We then demonstrate how the minimum bound can inform reader sensitivity specification to help ensure reliable inventory performance.Passive ultra-high frequency (UHF) RFID tags are dom-36 inating the RFID market, and most commodity UHF RFID. 34 • Fact 1: the power of backscattered RFID signals 35 is frequency-dependent. tags do not support cryptographic operations.
This article walks through the basics and advanced principles related to how UHF RFID Passive tags communicate via backscatter. Before reading, it is important to know about the types of coupling and when each one is used.In order to read multiple tags simultaneously, the tag and reader must be designed to detect the condition that more than one tag is active. Otherwise, the tags will all backscatter the carrier at the same time, and the amplitude-modulated waveforms shown in Figures 3 and 4 would be garbled. This is referred to as a collision.
We derive a theoretical formula for RCS of an RFID tag with a minimum scattering antenna and describe an experimental measurement technique which involves using a network analyzer connected to an anechoic chamber with and without the tag.
Since there is not enough field power to operate a traditional RF transmission, passive RFID tags communicate back to the reader with a technique called ‘backscatter’. In effect, what the tag does is alter the impedance of the antenna match so that more or less energy is reflected.
This paper proposed a novel tag circuit design for amplitude-shift keying (ASK) modulation. Instead of using the conventional resistive modulator, we proposed a reactive modulator for impedance matching and backscattered signal modulation. In the past two decades, point-to-point BackCom has been widely deployed in the application of radio-frequency identification (RFID) for a passive RFID tag to report an ID to an enquiring Reader over the near field (typically several centimeters).Traditional passive UHF RFID tags employ either ASK or PSK backscatter modulation to communicate data from memory or sensors on the tag to a remotely-located reader.RCID: Fingerprinting Passive RFID Tags via Wideband Backscatter Abstract: Tag cloning and spoofing pose great challenges to RFID applications. This paper presents the design and evaluation of RCID, a novel system to fingerprint RFID tags based on the unique reflection coefficient of each tag circuit.
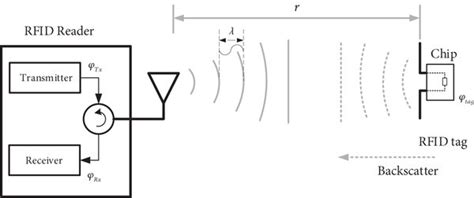
To validate this model, we propose a backscatter calibration device to enable measurements with estimated 0.5 dB uncertainty. We then demonstrate how the minimum bound can inform reader sensitivity specification to help ensure reliable inventory performance.
make a smart card reader work
Simple Radio, our free iOS and Android app. Continue listening to your favorite stations anytime, anywhere. KAHI Radio - KAHI, The Voice of the Foothills, AM 950, Auburn, CA. Live stream .
passive rfid tag backscatter|backscattering rfid tags